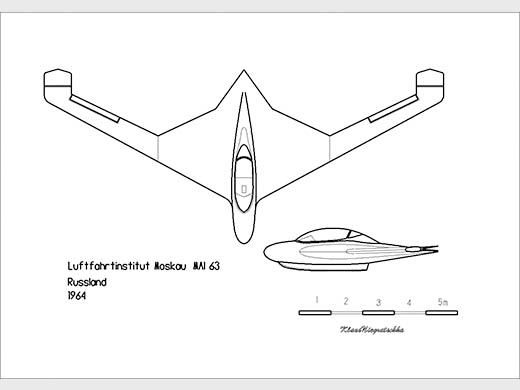
MAI-63
Autre nom (ou nom en langue originelle) : МАИ-63| DONNÉES GÉNÉRALES |
| Année du premier vol (ou de design, si seul projet) |
1964 |
| Pays | URSS |
| Designer(s) | KNIGHT, B. & BESPALOV, G. & TISHCHENKO, A. & VOLKOV, E. & TURIK, A. & TURCHKOV, S. & FATIANOV, V. & al. |
| Premier constructeur | MAI |
| Type d'appareil | Aile volante |
| Fonction | Expérimental |
| SPÉCIFICATIONS TECHNIQUES |
| Envergure | 12.6 m |
| Longueur | -- |
| Hauteur | -- |
| Allongement | 17.5 |
| Surface alaire | 9 m2 |
| Profil aile | Laminaire. |
| Masse à vide | 126 kg |
| Masse maxi | 200 kg |
| Charge alaire | 22.2 kg/m2 |
| Vitesse mini | -- |
| Vitesse maxi | -- |
| Finesse maxi | 35 |
| Taux de chute mini | 0.61 m/s |
| Nb sièges | 1 |
| Structure | Tout métallique |
AUTRES INFORMATIONS
| Constructeur(s) |
| ||||||
| Infos techniques | |||||||
| Histoire résumée | En 1963, les étudiants du MAI sous la direction d'Alexei Ivanovich Pietsuj ont conçu un planeur avec un schéma d'aile volante qui a été nommé MAI-63. V. Rytsariev, G. Bespalov, O. Tischenko, Ye se sont démarqués dans la construction du modèle. Volkov, A. Turik, S. Turchkov, V. Fatyanov, V. Vasiliev et V. Pushkin. Tous les travaux de construction ont été effectués par les étudiants eux-mêmes. Les tests ont commencé en 1964, ce qui a montré des problèmes de manque de résistance de la structure de l'aile. Après les premiers essais, plusieurs corrections ont été apportées à l'appareil: la structure de l'aile a été renforcée et des modifications ont été apportées au train d'atterrissage. In 1958, students of the Faculty of Aircraft A. Krivomlin, M. Aleksandrov, Yu Belov, A. Belosvet, V. Irinarkh, S. Kurylenko, E. Mizinov, V. Novikov and others joined in the SKB (Student Design Bureau) to build a "flying-wing" glider, LK-MAI. This was only a project and the MAI-63 design was based on the research done to develop LK-MAI. In autumn 1962 the members of ASK MAI (Aviation Sport Klub), the research section of which was headed by A. I. Pietsukh, began to develop the single seat "flying-wing" glider, MAI-63. In 1964 at the the studio laboratory of the department of design and engineering students under the leadership of A. I. Pietsukh built a glider. Students done all steel and assembly work on their own. Many of them hed working skills, as they were masters of the aeromodelling sport. MAI-63 tests were conducted in 1964 in Alferevo by glider testpilot A. I. Pietsukh. There have been several tow on the ground approaching take-off speed. Because of the lack of torsion rigidity of the wing no flights were done. After the tests the stiffness of the wing was increased and the structure was partially modified. In 1965, MAI-63 was modified to a motor-glider installing on a pole erected over the central part of the glider an air-cooled EP-760 23 HP, five-cylinder, two-stroke radial engine. The aim was to perform further tests by selflaunching. The engine was designed by Polyakov specifically for motor-gliders and light aircraft. The modified glider got the designation MAI-63M. Tests were conducted at the flying club's airport. The engine during the trial taxi runs was unstable so the powered version of the glider had never flown. | ||||||
| Liens personnalités | Pas de personnalité associée. |
SOURCES DOCUMENTAIRES
| Liens WEB | Site : 100 Jahre Nuflügel /A century of flying wings de Klaus Niegratschka . une photo [Lien mort]. (2020-05-06 CL) Site : Nuricom (Klaus Niegratschka) . Plan 3 vues [Lien mort]. (2020-05-06 CL) Site : Site Coin de Ciel (Уголок неба) . Texte + photo + specs. (2020-05-06 CL) Site : EcuRed . Note. (2020-05-06 CL) |
| Livres | Entsiklopediia Planery Rossii par KRASILSHCHIKOV, A. P. (2005) [p. 188, 251, 331. Note + specs]. Летательные аппараты МАИ par MAKAROV, Youri Vasilievich (1994) []. |
Team J2mcL © 2003 -
- Pages optimisées pour Mozilla Firefox